| 根據運行的環境,操作系統可以分為桌面操作系統,手機操作系統,服務器操作系統,嵌入式操作系統等。 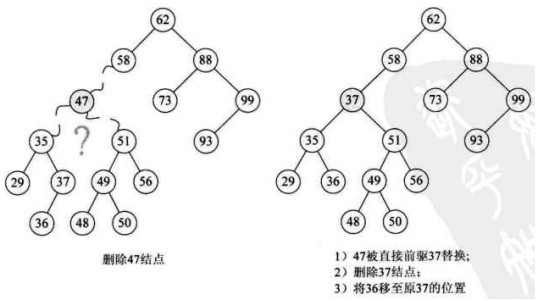
二進制排序樹是具有以下屬性的空樹或二進制樹:
(1)如果左子樹不為空,則左子樹上所有節點的值小于其根節點的值;
(2)如果右子樹不為空,則右子樹上所有節點的值都大于其根節點的值;
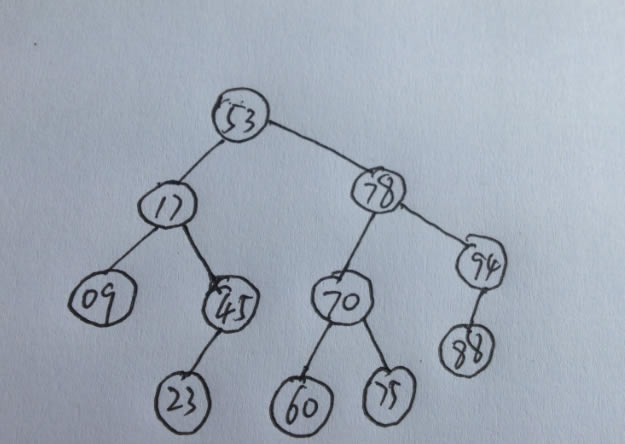
(3)左右子樹也是二進制排序樹;
(4)沒有節點具有相等的鍵值.
如下:
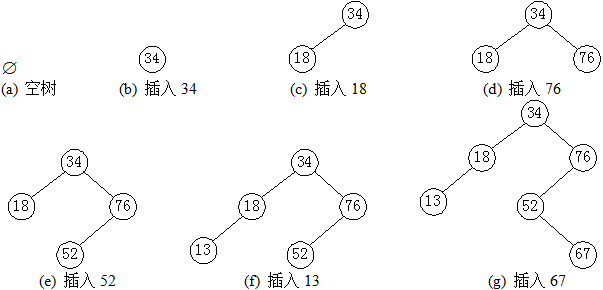
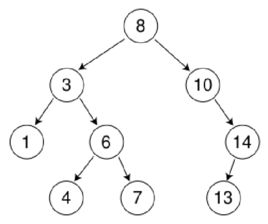
樹遍歷方法通常具有以下方法:
(1)層次遍歷: 按照樹的級別遍歷,如樹所示: 8、3、10、1、6、14、4、7、13
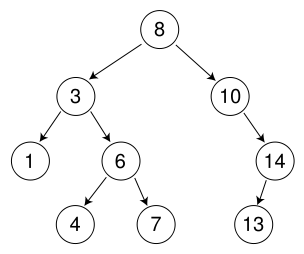
(2)順序遍歷: 節點遍歷順序為當前節點,左節點和右節點. 圖片樹: 8、3、1、6、4、7、10、14、13
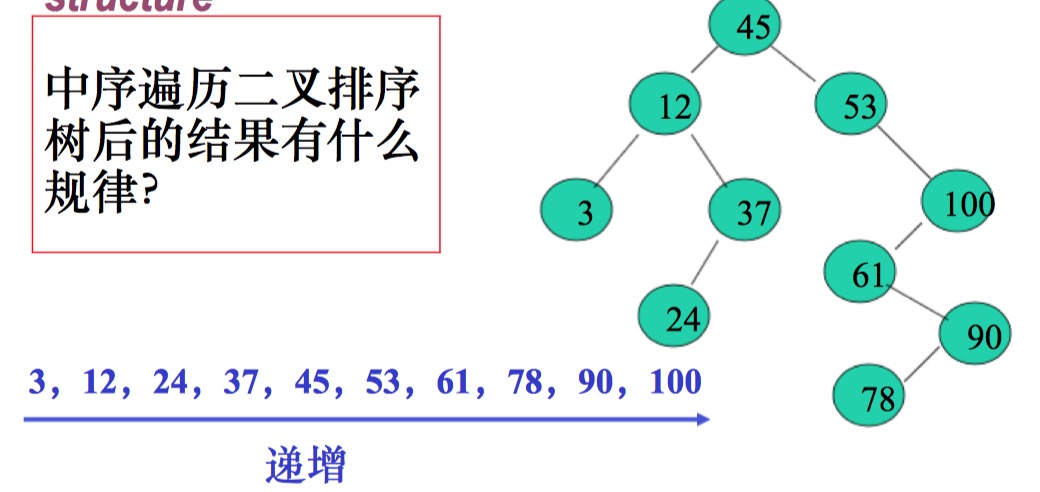
(3)中序遍歷: 節點遍歷順序為左節點,當前節點和右節點. 圖片樹: 1、3、4、6、7、8、10、13、14
(4)后續遍歷: 節點遍歷順序為左節點,右節點二叉排序樹的建立,當前節點. 如樹所示: 1,4,7,6,3,8,13二叉排序樹的建立,14,10
package com.lee.wait;
/**
* Node 二叉樹上的節點
* @author wait
*
*/
public class Node {
/**
* 節點的數據,這里我們用一個int表示
*/
public int data;
/**
* 節點的左孩子
*/
public Node left;
/**
* 節點的右孩子
*/
public Node right;
/**
* 構造函數,data初始化節點的值
* @param data
*/
public Node(int data){
this.data=data;
}
/**
* 默認構造函數,data=0
*/
public Node(){
this(0);
}
}
(2)二進制排序樹類BTree.java
package com.lee.wait;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* BTree二叉排序樹類
*
* @author wait
*
*/
public class BTree {
/**
* 樹的根節點
*/
public Node root;
/**
* 記錄樹的節點個數
*/
public int size;
/**
* 默認構造函數,樹的根節點為null
*/
public BTree() {
root = null;
size = 0;
}
/**
* 插入一個新的節點node
*
* @param node
*/
public void insert(Node node) {
if (root == null) {
root = node;
size++;
return;
}
Node current = root;
while (true) {
if (node.data <= current.data) {
if (current.left == null) {
current.left = node;
size++;
return;
}
current = current.left;
} else {
if (current.right == null) {
current.right = node;
size++;
return;
}
current = current.right;
}
}
}
/**
* 插入一個值為data的節點
*
* @param data
*/
public void insert(int data) {
insert(new Node(data));
}
/**
* 根據int數組里面的值建立一個二叉排序樹
*
* @param datas
*/
public void bulidTree(int[] datas) {
for (int i = 0, len = datas.length; i < len; i++) {
insert(datas[i]);
}
}
/**
* 返回二叉排序樹的層次遍歷的結果,使用通用的廣度優先遍歷方法
*
* @return 以int數組的形式返回結果
*/
public int[] layerOrder() {
int[] res = new int[size];
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>();
queue.offer(root);
int i = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node current = queue.poll();
res[i++] = current.data;
if (current.left != null) {
queue.offer(current.left);
}
if (current.right != null) {
queue.offer(current.right);
}
}
return res;
}
/**
* 先序遍歷二叉排序樹,非遞歸的方法,深度優先思想
*
* @return 以int數組的形式返回結果
*/
public int[] preOrder() {
int[] res = new int[size];
int i = 0;
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
Node node = root;
while (node != null) {
while (node != null) {
stack.push(node);
res[i++] = node.data;
node = node.left;
}
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek().right == null) {
node = stack.pop();
}
if(!stack.isEmpty()){
node=stack.pop();
if (node != null) {
node = node.right;
}
}else{
node=null;
}
}
return res;
}
/**
* 中序遍歷二叉排序樹 非遞歸的方法,深度優先思想
* @return
*/
public int[] inOrder() {
int[] res = new int[size];
int i = 0;
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
Node node = root;
while (node != null) {
while (node != null) {
stack.push(node);
node = node.left;
}
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek().right == null) {
node = stack.pop();
res[i++] = node.data;
}
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
node = stack.pop();
res[i++] = node.data;
if (node != null) {
node = node.right;
}
}else{
node=null;
}
}
return res;
}
/**
* 后序遍歷二叉排序樹 非遞歸的方法,深度優先思想
* @return
*/
public int[] postOrder() {
int[] res = new int[size];
int i = 0;
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
Node node = root;
Stack<Boolean> stackFlag=new Stack<Boolean>();
while (node != null) {
while (node != null) {
stack.push(node);
stackFlag.add(false);
node = node.left;
}
while (!stack.isEmpty() && (stack.peek().right == null||stackFlag.peek()==true)) {
node = stack.pop();
stackFlag.pop();
res[i++] = node.data;
}
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
node=stack.peek();
stackFlag.pop();
stackFlag.add(true);
if (node != null) {
node = node.right;
}
}else{
node=null;
}
}
return res;
}
/**
* 先序遍歷,遞歸方法實現
* @param node 當前訪問的節點
* @param list 存儲節點值的容器
*/
private void preOrderRe(Node node,List<Integer> list){
if(list==null){
list=new ArrayList<>();
}
if(node==null){
return;
}
list.add(node.data);
if(node.left!=null){
preOrderRe(node.left,list);
}
if(node.right!=null){
preOrderRe(node.right,list);
}
}
/**
* 先序遍歷,遞歸 調用上面實現函數
* @return
*/
public int[] preOrderRe(){
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
preOrderRe(root, list);
int[] res=new int[size];
for(int i=0,size=list.size();i<size;i++){
res[i]=list.get(i);
}
return res;
}
/**
* 中序遍歷,遞歸方法實現
* @param node 當前訪問的節點
* @param list 存儲節點值的容器
*/
private void inOrderRe(Node node,List<Integer> list){
if(list==null){
list=new ArrayList<>();
}
if(node==null){
return;
}
if(node.left!=null){
inOrderRe(node.left,list);
}
list.add(node.data);
if(node.right!=null){
inOrderRe(node.right,list);
}
}
/**
* 中序遍歷,遞歸 調用上面實現函數
* @return
*/
public int[] inOrderRe(){
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
inOrderRe(root, list);
int[] res=new int[size];
for(int i=0,size=list.size();i<size;i++){
res[i]=list.get(i);
}
return res;
}
/**
* 后序遍歷,遞歸方法實現
* @param node 當前訪問的節點
* @param list 存儲節點值的容器
*/
private void postOrderRe(Node node,List<Integer> list){
if(list==null){
list=new ArrayList<>();
}
if(node==null){
return;
}
if(node.left!=null){
postOrderRe(node.left,list);
}
if(node.right!=null){
postOrderRe(node.right,list);
}
list.add(node.data);
}
/**
* 后序遍歷,遞歸 調用上面實現函數
* @return
*/
public int[] postOrderRe(){
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
postOrderRe(root, list);
int[] res=new int[size];
for(int i=0,size=list.size();i<size;i++){
res[i]=list.get(i);
}
return res;
}
}
(3)測試代碼TestBTree.java
本文來自本站,轉載請注明本文網址:
http://www.pc-fly.com/a/jisuanjixue/article-252817-1.html
| 
